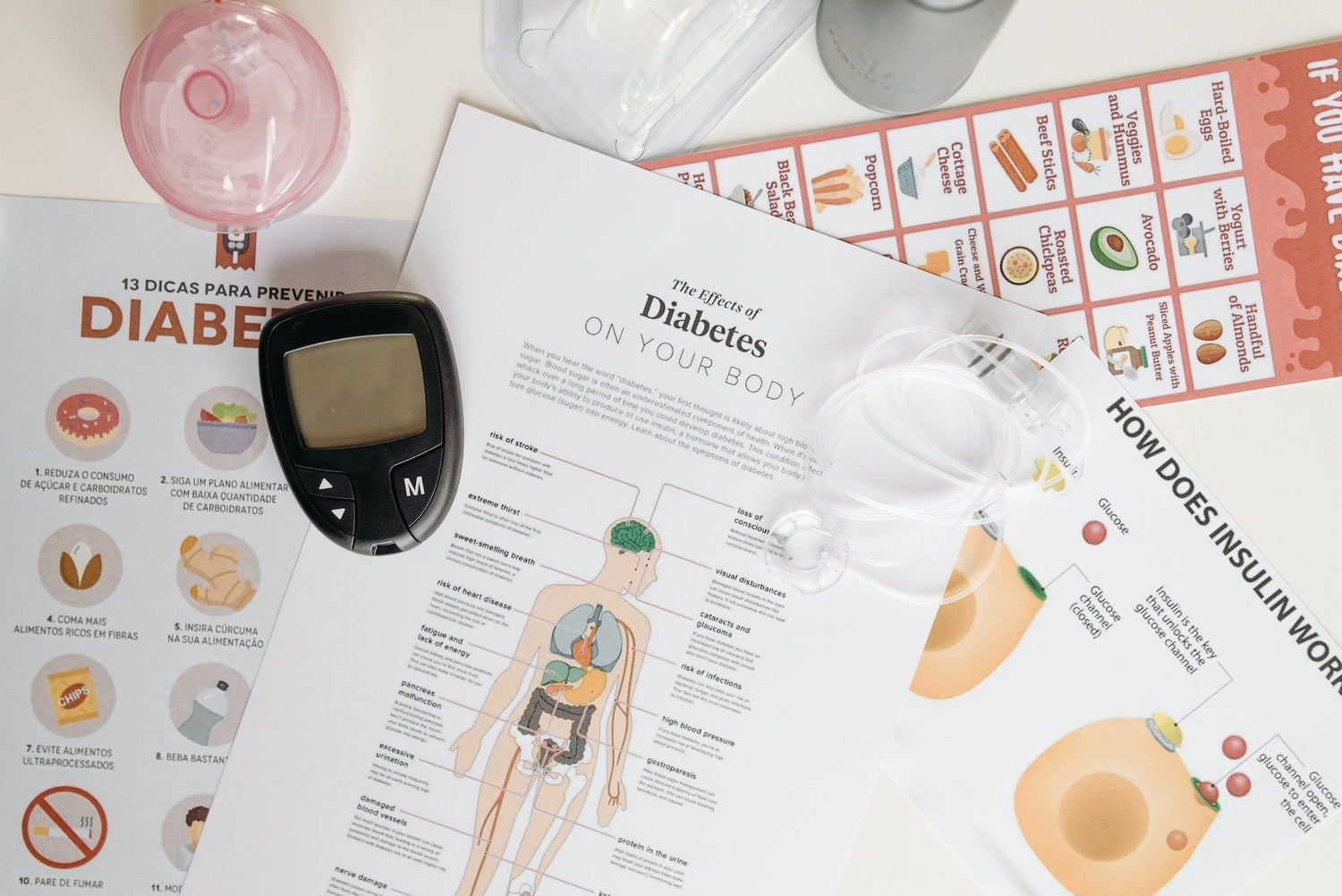
Diabetes Demystified: History, Types, Control & Diet Tips
Diabetes Demystified: History, Types, Control & Diet Tips
Introduction
Diabetes is a chronic health condition affecting millions worldwide. With rising cases, understanding diabetes—its history, types, diagnosis, and management—is crucial. Whether you're newly diagnosed or supporting a loved one, this guide covers everything from glucometer use to the best (and worst) foods for diabetes control.
A Brief History of Diabetes
Diabetes has been known since ancient times. The term "diabetes" was first used by the Greek physician Aretaeus in the 1st century AD, describing it as a condition causing excessive thirst and urination.
- 1500 BC: Egyptian manuscripts mention a disease with frequent urination.
- 5th Century AD: Indian physicians identified diabetes and linked it to sweet-tasting urine.
- 18th-19th Century: Scientists discovered the role of the pancreas and insulin.
- 1921: Frederick Banting and Charles Best successfully used insulin to treat diabetes, revolutionizing its management.
Types of Diabetes
There are three main types of diabetes:
1. Type 1 Diabetes – An autoimmune condition where the pancreas produces little or no insulin. Usually diagnosed in children and young adults.
2. Type 2 Diabetes – The most common type, where the body becomes insulin resistant. Linked to obesity, poor diet, and inactivity.
3. Gestational Diabetes – Occurs during pregnancy and usually resolves after childbirth but increases future diabetes risk.
How is Diabetes Diagnosed?
Doctors use several tests to diagnose diabetes:
- Fasting Blood Sugar Test – Measures glucose after an 8-hour fast. Normal: <100 mg/dL | Diabetes: ≥126 mg/dL
- HbA1c Test – Average blood sugar over 2-3 months. Normal: <5.7% | Diabetes: ≥6.5%
- Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT) – Checks blood sugar before and after a sugary drink. Diabetes: ≥200 mg/dL after 2 hours
- Random Blood Sugar Test – Diabetes: ≥200 mg/dL with symptoms
How to Control Diabetes?
Managing diabetes involves lifestyle changes, medication (if needed), and regular monitoring.
✅ Monitor Blood Sugar – Use a glucometer to track levels.
✅ Eat a Balanced Diet – Focus on fiber, protein, and healthy fats.
✅ Exercise Regularly – 30 minutes daily improves insulin sensitivity.
✅ Medication/Insulin – Follow your doctor’s prescription.
✅ Stay Hydrated & Reduce Stress – Both impact blood sugar levels.
Why a Glucometer is Worth It?
A glucometer is a must-have for diabetics. Here’s why:
✔ Instant Blood Sugar Readings – Helps adjust diet and medication.
✔ Tracks Progress – Identifies patterns (highs/lows).
✔ Prevents Emergencies – Alerts you to dangerous spikes or drops.
✔ Encourages Better Control – Immediate feedback keeps you accountable.
If you want to buy a glucometer at discounted wholesale price checkout here
Tip: Check levels fasting, before meals, and 2 hours after eating.
Best Diet to Control Diabetes
A diabetes-friendly diet includes:
- High-Fiber Foods – Oats, whole grains, beans, vegetables.
- Lean Proteins – Chicken, fish, tofu, eggs.
- Healthy Fats – Avocados, nuts, olive oil.
- Low-Glycemic Fruits – Berries, apples, pears.
- Non-Starchy Veggies – Spinach, broccoli, cucumbers.
Foods to Avoid
❌ Sugary drinks (soda, fruit juices)
❌ Refined carbs (white bread, pastries)
❌ Fried & processed foods
❌ High-sugar fruits (mangoes, grapes)
❌ Trans fats (packaged snacks)
Final Thoughts
Diabetes is manageable with the right knowledge and habits. Regular monitoring, a balanced diet, exercise, and medical guidance can help you live a healthy, active life.
Got diabetes? Take control today—your health is worth it!
Would you like any personal experiences or expert quotes added to this blog? Let me know how I can enhance it further! 😊
Legal Disclaimer: Consult your doctor before taking any medication or a treatment, do not do self medication, this article is only for educational and knowledge purpose and author has not advised or prescribed any treatment or medication.